Electric vehicles (EVs) are transforming transportation, and their integration with home energy systems offers significant advantages. By combining EVs with renewable energy sources and smart energy management, homeowners can optimize electricity use, reduce costs, and increase energy resilience. This guide explores the methods, benefits, technologies, and considerations for integrating electric vehicles with home energy systems.
Understanding EV Integration with Home Energy Systems
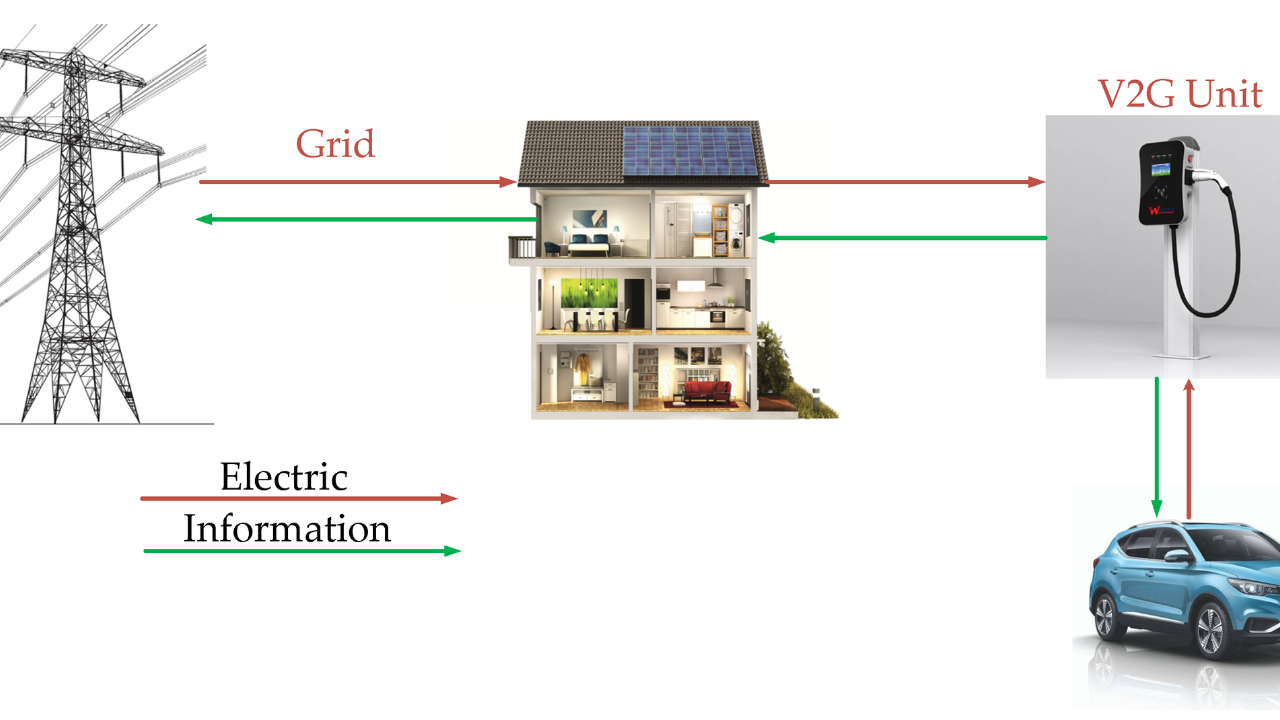
Integrating an EV with a home energy system involves using the vehicle not only for transportation but also as a mobile energy storage unit. Modern EVs, particularly those with bi-directional charging capability, can store electricity from solar panels or the grid and supply it back to the home when needed. This approach enhances energy efficiency and flexibility.
Key Concepts:
- Vehicle-to-Home (V2H): The EV provides power directly to the home during peak demand or outages.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): EVs supply stored energy back to the utility grid, potentially earning credits.
- Smart Charging: Optimizes charging schedules to take advantage of renewable energy production or off-peak electricity rates.
Benefits of Integrating EVs with Home Energy
- Reduced Electricity Costs
- Use solar-generated electricity to charge EVs instead of drawing from the grid.
- Avoid high peak-hour electricity rates through smart charging and V2H usage.
- Backup Power Supply
- EV batteries can provide emergency power during blackouts or grid failures.
- Ensures critical home systems, such as refrigeration, lighting, and heating, remain operational.
- Increased Use of Renewable Energy
- Charging EVs during solar production times maximizes renewable energy consumption.
- Reduces reliance on fossil-fuel-based electricity.
- Grid Support and Incentives
- V2G programs allow homeowners to sell stored electricity back to the grid, generating revenue or credits.
- Supports grid stability by supplying power during high-demand periods.
- Environmental Impact
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions by combining EV use with renewable electricity.
Technologies Needed for Integration
| Technology | Function | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bi-Directional Chargers | Enable V2H and V2G energy flow | Provides home backup and grid support |
| Solar Panels | Generate renewable electricity at home | Reduces reliance on the grid |
| Home Battery Storage | Stores excess electricity for later use | Complements EV and solar energy use |
| Smart Energy Management | Optimizes charging and energy usage | Minimizes electricity costs and maximizes efficiency |
| EV with Sufficient Battery Capacity | Serves as mobile energy storage | Supports home energy needs during outages |
Implementation Steps
- Assess Energy Needs
- Calculate household electricity consumption and determine EV battery requirements.
- Consider daily driving distances to ensure sufficient vehicle range.
- Install Compatible Equipment
- Bi-directional chargers for V2H and V2G functionality.
- Solar panels and home batteries to store excess energy.
- Connect and Configure Smart Systems
- Use energy management software to schedule EV charging and discharging.
- Integrate with smart home devices for maximum efficiency.
- Monitor Usage and Optimize
- Track energy consumption, solar generation, and EV battery levels.
- Adjust charging times based on peak usage, electricity rates, and renewable availability.
Cost Considerations
| Component | Typical Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Bi-Directional Charger | $1,500–$5,000 | Enables V2H and V2G functionality |
| Home Battery Storage | $5,000–$15,000 | Supports energy backup and renewable integration |
| Solar Panel System | $10,000–$30,000 | Provides clean electricity for EV charging |
| Smart Energy Management System | $500–$2,000 | Optimizes charging, discharging, and energy usage |
Tip: Incentives and rebates for EV charging, solar installation, and battery storage can significantly reduce upfront costs.
Challenges and Considerations
- Battery Degradation: Frequent V2H or V2G use may slightly reduce battery lifespan.
- Upfront Costs: Initial investment in chargers, solar panels, and batteries can be high.
- Grid Compatibility: Not all utilities support V2G programs; check local regulations.
- Technical Expertise: Installation and system configuration require professional support.
Overview Table
| Feature | Description | Benefit to Homeowner |
|---|---|---|
| Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) | Uses EV battery to power home | Backup power during outages |
| Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) | Supplies electricity to the utility grid | Earn credits and support grid stability |
| Solar Integration | Charges EV with renewable energy | Reduces electricity bills |
| Smart Charging | Optimizes charging based on demand and cost | Minimizes energy costs and maximizes efficiency |
| Home Battery Storage | Stores excess electricity for use | Complements EV and renewable energy use |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces fossil fuel consumption | Lowers carbon footprint |
Conclusion
Integrating electric vehicles with home energy systems represents a smart, sustainable approach to modern living. By leveraging V2H, V2G, solar energy, and smart management, homeowners can reduce costs, enhance energy security, and maximize the use of renewable energy. While there are upfront costs and technical considerations, the long-term benefits—both economic and environmental—make this integration a compelling choice for energy-conscious households.
3 Quick FAQs
- Can my EV power my home during a blackout?
Yes, with a bi-directional charger and compatible energy system, your EV can serve as backup power. - Does V2G affect EV battery life?
Minimal impact occurs if used correctly; modern EVs are designed to handle bidirectional energy flow. - Can I integrate solar panels with my EV charging?
Absolutely—solar energy can charge your EV, reducing reliance on the grid and lowering electricity bills.